While there are obvious advantages to moving to the cloud, there are also risks. There are numerous factors that must be considered. For example, you must minimise the impact of the migration on end users, minimize service downtime, determine which application/services should be migrated and, if necessary, provide cloud platform training to the organization’s IT employees.
You must first identify the challenges you may face in order to prepare adequately. A full examination of probable roadblocks can be found below.
- Fail to plan appropriately. You may run into big issues if your objectives aren’t well stated, or if you don’t specify which application, services, data and migrations should be transferred.
- Failure to consider vendor lock-in: If you develop a strong relationship with a single vendor, you may face significant difficulties if you need to move vendors in the future. suggested to use multi cloud or multi vendor platform
- Lack of awareness about security issues: When sensitive data is transferred to the cloud, many security teams do not exercise sufficient caution.
- Failing to assess the expenses of a cloud strategy: Many businesses are attracted to cloud computing due to its inexpensive costs.
- Fail to design a disaster recovery plan: It’s critical to be aware of the hazards. Check to see if your vendor has a disaster recovery plan in place.
Here are some steps to tackle the challenges of cloud migration:
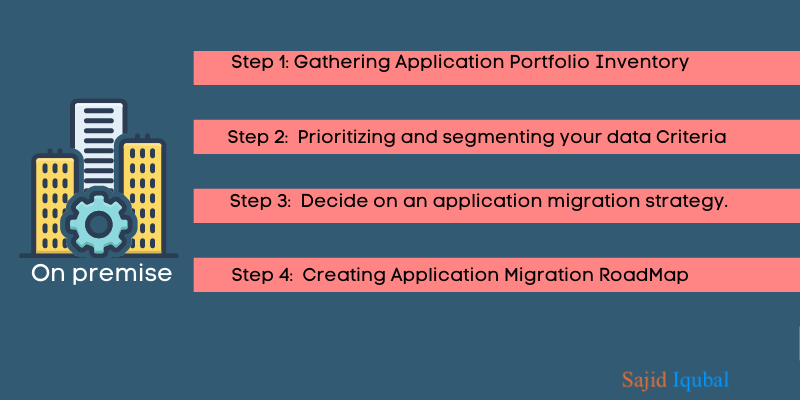
Step1: Gathering Application Portfolio Inventory
- Organizing an application discovery workshop
- Interviewing the owner of the application
- Implement discovery using a tool.
Step 2: Prioritizing and segmenting your data Criteria
- Identifying complexity
- Criticality and preferences by profiling application inventory
- Prioritizing and clustering
Step 3: Decide on an application migration strategy.
- Prioritization, expertise, and best practices are all driving factors.
- Make the most of your patterns.
- Interdependence should be captured.
- From ‘lift and shift’ to ‘drop and shop,’ we’ve got you covered.
Step 4: Creating Application Migration RoadMap
- Expect a complete IT overhaul.
- Changes in IT processes and organisational
- Change management should be included.
- Concentrate on a new operational model.
Migration and disposition options:
Retain: This is the option of “doing nothing.” Obsolescence expenses often rise over time as legacy expenditures remain constant.
Retire: As needed, decommission and archive application/data.
Rehost: ‘Lift and Shift’ or “Forklifting” are two terms for the same thing. Migrations that are automated and scripted are extremely effective.
Repurchase: Either a purchase replacement or/and an upgrade.
Replatform: Possibilities to address major infrastructure upgrades. It is possible to achieve this, which has a good impact on compliance, regulatory, and obsolescence drives.
Refactor: Re-architecting and recoding necessitate the acquisition of new skills. There’s a chance that there’ll be a lot of business disruption.